Imagine this: a storm rages, the lights flicker, then plunge your home into darkness. While your neighbors fumble for flashlights, your house seamlessly transitions to backup power, often before you even notice the outage. That's the magic of a standby generator, a permanently installed guardian that automatically restores electricity during disruptions. But achieving this level of dependable, safe operation hinges entirely on professional installation and wiring of standby generators. This isn't a weekend DIY project; it's a critical investment in your home's safety and comfort, demanding expert knowledge of electrical systems, fuel lines, and local building codes.
With the average U.S. home experiencing 1.3 power outages per year, ensuring your backup system is installed correctly is paramount. Let's delve into what makes a professional installation not just recommended, but essential.
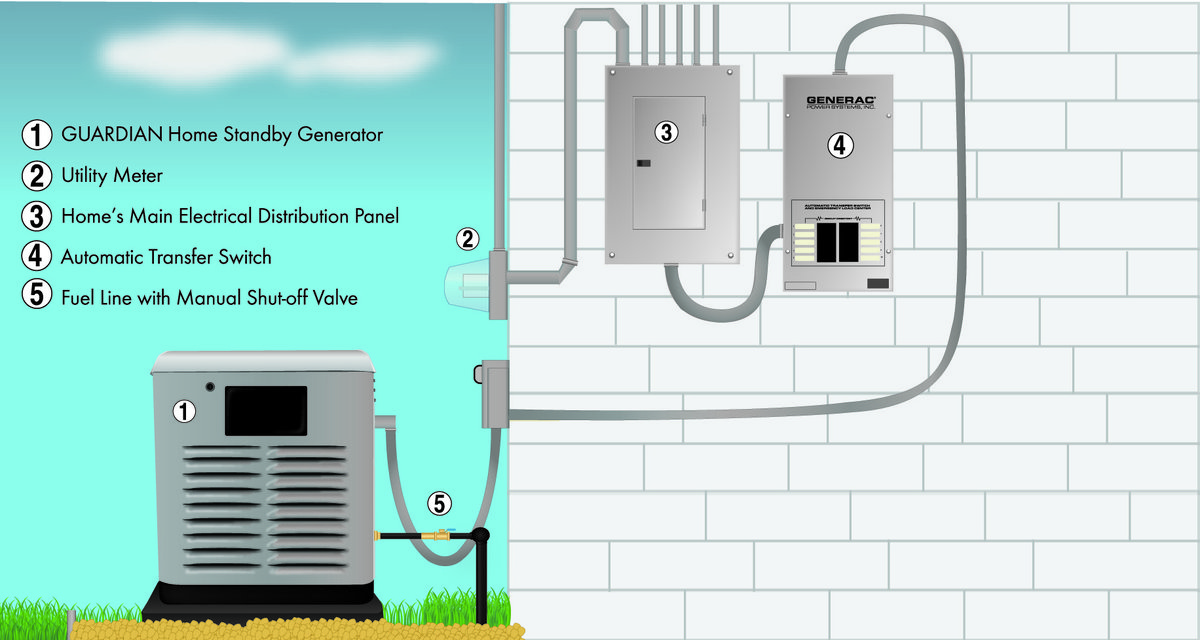
At a Glance: Your Standby Generator Installation Essentials
- Safety First: High-voltage electricity and combustible fuels demand expert handling; professional installation is non-negotiable for safety.
- Permits are Mandatory: Always secure local electrical, fuel, and zoning permits before installation to avoid fines and ensure compliance.
- Strategic Placement: Generators need specific clearance from windows, doors, and vents to prevent carbon monoxide exposure and allow airflow.
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): This vital component detects outages and safely switches your home's power source.
- Fuel & Electrical Expertise: Connecting fuel lines and integrating the generator into your home's electrical panel requires specialized skills and adherence to strict codes.
- Testing is Key: A professional will thoroughly test the system to ensure it activates correctly and transfers power flawlessly during a simulated outage.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Even after expert installation, regular maintenance is crucial for long-term reliability.
Beyond the Blackout: Understanding Your Home's Power Lifeline
A standby generator isn't just a big engine; it's a sophisticated system designed to protect your peace of mind. Connected directly to your home's electrical system, it patiently waits for an outage. When utility power falters, an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) acts as the brain, detecting the disruption and activating the generator within seconds. Once running, the ATS safely switches your home's power supply from the grid to the generator, keeping your lights on, fridge cold, and essential appliances running. When grid power returns, the ATS reverses the process, shutting down the generator.
Standby generators typically run on one of three common fuel types:
- Natural Gas: Connected directly to your home's gas line, this option offers continuous, unlimited runtime without the need for refueling. It’s often the most convenient choice where natural gas is available.
- Propane: Stored in a dedicated tank, propane is an excellent choice for homes off the natural gas grid. It's clean-burning and easily stored, though tank size will dictate runtime.
- Diesel: Known for its power and efficiency, diesel generators are robust and suitable for larger homes or longer durations. They require a dedicated fuel storage tank.
Each type has its nuances, but the installation principles for safety and compliance remain universal.
The Unseen Risks: Why DIY is Dangerous for Generator Wiring and Fuel
We get it. The allure of saving money on a big project is strong. However, when it comes to the high-voltage electricity and combustible fuels involved in standby generator installation, professional expertise isn't just a recommendation—it's a critical safety measure. Attempting to install the electrical and fuel connections yourself can lead to:
- Electrocution: Direct contact with high-voltage wiring can be fatal.
- Fires and Explosions: Improperly connected fuel lines are a significant fire hazard. Gas leaks, in particular, can be undetectable without proper testing and extremely dangerous.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Incorrect generator placement or exhaust routing can allow this deadly, odorless gas to seep into your home.
- Damage to Appliances: Faulty wiring can cause power surges or inconsistent voltage, frying sensitive electronics.
- Voided Warranties & Insurance Issues: Most manufacturers will void warranties if installation isn't done by a certified professional. Insurance companies may also refuse claims stemming from DIY mishaps.
- Legal Penalties: Local codes and regulations are strict for a reason. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines, mandatory re-installation, or even legal action if an incident occurs.
Addressing any underlying electrical issues with a licensed electrician before installing a backup generator is also crucial, ensuring your home's existing system can safely integrate with the new power source.
Navigating the Installation Journey: A Professional's Blueprint
While every home and generator model has specific requirements, the core steps of a professional standby generator installation follow a well-defined process, prioritizing safety and efficiency.
Step 1: Laying the Groundwork – Permits & Planning
Before a single shovel hits the ground or a wire is connected, the first and most critical step is navigating the local bureaucracy. Your professional installer will assist with:
- Permit Acquisition: This isn't optional. You'll need permits from your local building department covering electrical, fuel, and often zoning aspects. These ensure your installation adheres to safety codes, minimum setbacks, and environmental regulations.
- Site Assessment: A qualified technician will visit your home to assess the best location for the generator, considering proximity to existing fuel lines, your electrical panel, and appropriate clearances.
Failure to secure the necessary permits can result in fines, forced removal, or expensive reinstallation, so this foundational step is never skipped.
Step 2: Choosing the Perfect Spot – Site Preparation
The chosen location for your generator is vital for both safety and performance. Professionals adhere to strict guidelines:
- Safe Clearance: The generator must be placed at least five feet away from all windows, doors, and vents to prevent carbon monoxide exhaust from entering your home. Adequate airflow around the unit is also essential for cooling and proper operation.
- Solid Foundation: The ground must be cleared and leveled. A sturdy concrete pad or a compacted gravel base is then installed to provide a stable, vibration-reducing foundation. Proper drainage is also ensured to prevent water accumulation around the unit.
This meticulous preparation prevents future issues and ensures the generator operates safely and efficiently for years to come.
Step 3: Anchoring Your Powerhouse – Positioning the Generator
Once the site is prepared, the heavy work begins. The generator unit is carefully moved and positioned onto its prepared foundation.
- Precise Placement: It's crucial that the generator sits perfectly level to prevent unnecessary vibrations, which can lead to premature wear and tear.
- Optimized Proximity: Professional installers strategically position the unit close to both your home's main electrical panel and the fuel source. This minimizes the length (and cost) of electrical wiring and fuel lines, improving overall efficiency and reducing potential points of failure.
Step 4: The Brain of the Operation – Installing the Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS)
The Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) is the heart of your generator's automation. It’s what makes your backup power seamless.
- Main Breaker Deactivation: The first safety measure is always to turn off the main breaker to your home, completely cutting power to the electrical panel.
- Strategic Mounting: The ATS is mounted near your home’s main electrical panel, often inside, but sometimes outdoors depending on the model and local codes.
- Conduit and Grounding: Conduit is run from the ATS location to the generator, protecting the electrical wiring that will connect the two. All connections within the ATS are secured, and it is properly grounded to protect against surges and electrical faults.
Step 5: Fueling the Fire – Connecting the Supply
This step involves highly combustible materials, underscoring the need for certified professionals.
- Absolute Safety: The fuel supply is shut off completely before any work begins. Crucially, no smoking or open flames are permitted anywhere near the work area.
- Leak-Proof Connections: The generator is connected to its dedicated fuel source—whether a natural gas line or a propane/diesel tank—using appropriate, code-compliant fittings, pipe sealant, or specialized tape. A readily accessible shut-off valve is also installed.
- Thorough Leak Detection: Once connections are made, the fuel supply is carefully turned back on. Professionals meticulously check for leaks using a soapy water solution (bubbles indicate a leak) or a specialized gas detector, ensuring a completely sealed and safe system.
Step 6: Weaving the Electrical Web – Wiring Your System
This is where the generator becomes fully integrated into your home's electrical grid. Again, all power must be off at the main breaker.
- Seamless Integration: Electrical wiring, including appropriate circuit breakers, is run from the generator to the ATS, and then from the ATS to your main electrical panel. This complex network must be installed according to National Electrical Code (NEC) standards and local regulations. Getting this right is crucial for the safe and reliable operation of your entire system. For detailed insights into this connection, you might find our guide on wiring a generator to your house helpful.
- Voltage Verification: Throughout the process, professionals use multimeters and voltage testers to verify correct voltage levels at various points, ensuring the system is delivering power safely and within specification.
- Secure & Grounded: All wiring is secured within conduit and junction boxes, and proper grounding is established, which is critical for preventing electrical hazards and protecting your home from power surges.
Step 7: Safeguarding Your System – Proper Grounding
Beyond the general electrical grounding, the generator itself requires specific grounding.
- Dedicated Ground Rod: A grounding rod is driven deep into the soil near the generator unit.
- Corrosion-Free Connections: Copper wiring connects the generator’s grounding terminal directly to this rod. All connections are secured and protected against corrosion, as required by electrical codes, to provide effective surge protection and prevent electrical shock hazards.
Step 8: Powering the Start – Battery Installation
For generators equipped with an automatic start feature (which most standby units are), a battery is essential.
- Manufacturer Specifications: The battery is connected precisely according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring clean and secure terminals for reliable power delivery.
- Essential Maintenance: Professionals will advise you on the importance of regularly charging and maintaining this battery, as it’s the immediate source of power for the generator's starter motor.
Step 9: The Grand Finale – Testing & Final Inspection
With all connections made, the system is ready for its critical trial run. This final stage is crucial to confirm everything works as expected.
- Simulated Outage: The main power supply to your home is deliberately turned off to simulate an outage.
- System Verification: The installer observes closely to ensure the ATS automatically detects the power loss, starts the generator within seconds, and flawlessly transfers power to the connected appliances in your home. They will also verify that the ATS correctly transfers power back to the grid and shuts down the generator once utility power is restored.
- Comprehensive Checks: A final inspection involves checking for any fuel leaks (even tiny ones), unusual noises, or warning lights from the generator. The installer confirms the generator remains level, fuel lines are secure, and that you, the homeowner, understand the basic operation and essential maintenance requirements.
Beyond Installation: Ensuring Long-Term Reliability and Safety
Installing a standby generator is a significant step, but ensuring its readiness for years to come involves ongoing vigilance.
Essential Warnings to Always Heed:
- NEVER DIY Fuel or Electrical Connections: We cannot stress this enough. The risks of high-voltage electricity and combustible fuels are too severe. Always rely on licensed and certified professionals for these critical connections.
- Adhere to All Codes: Local electrical codes and regulations are not suggestions; they are mandates designed for your safety. A professional installer ensures your system is compliant, preventing hazards, fines, and the costly requirement for reinstallation.
- Fuel Safety is Paramount: Beyond the initial installation, never smoke or use open flames near your generator's fuel lines or tank. Store fuel safely and responsibly if you have a diesel or propane unit.
- Address Existing Electrical Issues: Before even considering a generator, have a licensed electrician address any underlying or pre-existing electrical problems in your home. A generator is only as safe as the system it's connected to.
Ongoing Care and Maintenance:
Even the most expertly installed generator needs regular attention to perform when you need it most. Follow your manufacturer’s guidelines for: - Scheduled Servicing: This typically includes routine oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug checks.
- Battery Maintenance: Ensure the battery remains charged and its terminals are clean and corrosion-free.
- Regular Load Testing: Periodically running your generator under load simulates an actual outage, ensuring all components are functional and ready. Many modern standby generators perform self-tests automatically.
Treating your standby generator as a set-it-and-forget-it appliance is a recipe for disaster. Regular, professional maintenance is the best way to protect your investment and guarantee power when you need it most.
Common Questions & Misconceptions About Professional Generator Installation
Even with comprehensive information, some questions naturally arise. Let's tackle a few:
"Can I really not install the electrical and fuel lines myself?"
Absolutely not. While you might be handy, the intricacies of high-voltage electrical wiring (connecting to your main panel) and the dangers of combustible fuel lines (natural gas, propane, diesel) require specialized certifications, tools, and an intimate knowledge of stringent safety codes. This is not a task for even experienced DIYers.
"What's the difference between a standby generator and a portable one, concerning installation?"
A standby generator is a permanently installed unit, hard-wired into your home's electrical system via an ATS, and connected directly to a continuous fuel source. A portable generator, conversely, is a temporary solution that needs to be manually hooked up (usually via an extension cord and often a manual transfer switch) and refueled. Standby generators offer automatic, hands-free operation and significantly higher power output, necessitating complex installation.
"How long does professional installation typically take?"
The timeline varies based on your home's existing infrastructure, the generator model, and local permit processes. Generally, once permits are approved and the site is ready, the physical installation can take anywhere from one to three days. However, the entire process, including permits and site preparation, can extend over several weeks.
"Are there any special considerations for installing generators in cold climates?"
Yes. In cold climates, installers pay extra attention to fuel line insulation, battery warmers, and ensuring the generator enclosure can withstand harsh weather. Propane tanks, in particular, may require specific placement to ensure proper vaporization.
Your Next Step Towards Uninterrupted Power
Investing in a standby generator is investing in the security and comfort of your home. But the true value of that investment is realized only when the system is installed correctly, safely, and compliantly by certified professionals. Don't compromise on safety or reliability.
Your next step should be to:
- Consult Licensed Professionals: Seek out reputable, certified electricians and generator installers in your area.
- Obtain Multiple Quotes: Compare services, experience, and pricing.
- Prioritize Safety & Compliance: Ensure your chosen installer is fully licensed, insured, and committed to adhering to all local and national codes.
With professional installation and proper maintenance, your standby generator will be ready to protect your home from the inconvenience and disruption of power outages, providing dependable backup power for years to come.